What is Forex(FX) and how does it works?
Trading forex involves buying one currency and selling another simultaneously. Through careful analysis, traders predict the potential direction of currency prices and attempt to capture gains based on price fluctuations. There is no centralised exchange for forex trading. Rather, it takes place electronically or online, between networks of global computers.
The market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.

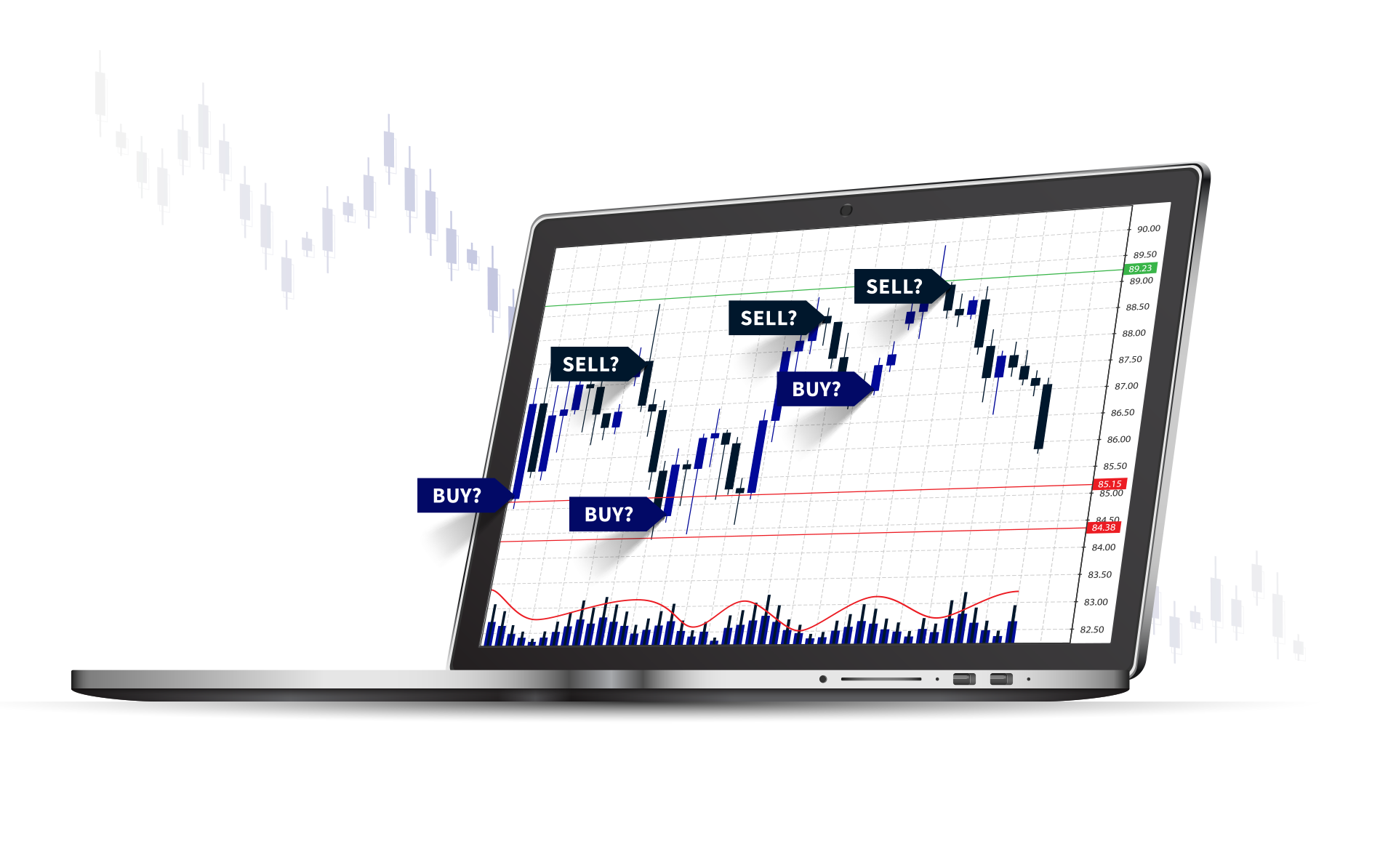
How do Forex Markets Work?
Forex is the most popular over-the-counter (OTC) market. In forex, currencies are bought and sold through a network of banks. As there is no exchange, forex trading is decentralised and trading can take place 24 hours per day. There are 4 main trading sessions, namely Sydney, London, New York and Tokyo.
The most popular forex market type is the spot forex market. In forex, spot trades involve the exchange of currency pairs electronically using an online trading platform. Other market types include the forward forex market and futures forex market.
The 4 major trading sessions
SYDNEY
3:00pm to
12:00am EST
TOKYO
7:00pm to
4:00am EST
LONDON
3:00am to
11:00am EST
NEW YORK
8:00am to
5:00pm EST
What Influence the Forex Market?
There are a number of factors that have an impact on the forex market.
They can split into two categories; market participants and macroeconomic factors.
Market Participants
Super Banks
As it is decentralised, it is the world's largest banks that determine the exchange rate. Global banks such as Barclays, HSBC, Citi, JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank are among the biggest traders of forex.
International Companies
Large global corporations are involved in the foreign exchange market for the purpose of doing business. If an Australian-based company is selling products in the United States they will have to trade USD to AUD in order to return their income back home.
Retail Traders
Refers to individuals who trade their own money in order to make a profit. Easier access to the forex market through online brokers and advanced trading platforms has resulted in retail traders accounting for a growing proportion of the forex market.
Economic & Macroeconomic Factors
Central Banks
Macroeconomic statistics such as inflation have a significant impact on forex markets. Governments and central banks such as the Federal Reserve meet on a regular basis to evaluate the status of their respective economies, set interest rates and monetary policy - all of which have a direct impact on forex markets.
Capital Markets
The prices of stock, bond and commodity futures also have an influence on foreign exchange markets.
International Trade
Figures relating to the trade numbers of a country have an impact on the value of currency. Trade deficits and surpluses will be reflected by price movements in the forex market.
Politics
This is particularly the case around key political events such as elections and results in high levels of volatility in the forex market. This is evident by historical events such as Brexit in the United Kingdom and numerous presidential election campaigns in the United States.
Position Size
When you decide on your position size, a term you will hear is “lot.” Lots are standardised position sizes for currencies. The forex market gives you the flexibility to trade according to your means and risk profile. The standard size for a lot is 100,000 units of the base currency. There also are mini and micro lot sizes that contain 10,000 and 1,000 units of the base currency, respectively.

What is Liquidity in Forex Trading?
Liquidity in the forex market refers to the ability of a currency to be bought or sold on demand. When you trade in major currency pairs, there are a lot of buyers and sellers in the market. This means that there is always likely to be an opposite player for every position you take. You can buy or sell large amounts of these currencies without causing any significant difference to the exchange rate.
Liquidity fluctuates during trading sessions. You are likely to see significant activity during the overlapping of the New York and London sessions.
Liquid markets, such as forex, tend to fluctuate by smaller increments, since high liquidity means less volatility. However, high volatility can occur due to significant external events.
Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Using guesswork to predict the direction of price movement is not the best idea. Experienced traders carefully conduct market analysis, in order to determine the direction in which currency rates are likely to move. Two major approaches are used here: fundamental analysis and technical analysis.
Fundamental Analysis
Currency values fluctuate according to a nation’s perceived economic health. Fundamental analysis is the study of all factors that impact a country’s economy and is also representative of its future trends. When investors perceive a particular economy as being more rewarding than others, demand for the domestic currency increases, driving up its price. Fundamental traders look out for these indicators to gauge the economic health of a country.
Monetary Policy
The interest rates decided by a country’s central bank directly impact the domestic currency. When the interest rate increases, currency value tends to appreciate and vice versa.
Inflation Rate
Central banks are responsible for keeping inflation in check and promoting employment. To do so, they have various tools available, including the nation’s monetary policy, market interventions and quantitative easing.
Balance of Trade
The balance between a country’s exports and imports can impact currency values.
GDP Growth
The overall health of an economy is denoted by its GDP growth. Currency values tend to appreciate with a favourable GDP growth rate.
There are several other economic indicators, like employment rate, retail sales, manufacturing index and housing market data, that impact the forex market. To keep track of the economic releases, traders use an economic calendar. This is because significant volatility tends to ensue on the days that important reports are released. Based on whether the actual figures meet or beat market consensus, currency prices can go up or down.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is based on the principle that the markets tend to repeat their historical price trends. To discover these trends, traders rely on technical indicators and forex chart analysis. Technical indicators are actually statistical formulae that can provide important information about the market. They are categorised into:
Trend
Such as Simple Average, Trend lines, Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Volume
Such as On Balance Volume (OBV), Chaikin Money Flow
Momentum
Such as Stochastic Oscillators, Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Volatility
Such as Average True Range (ATR), Volatility Index (VIX)
These platforms also allow you to use a combination of both fundamental and technical analysis. While fundamental analysis, through financial news alerts, allows traders to gauge the interest rate and inflation outlook for both currencies in a pair, technical indicators and charts provide insight into trends and ranges within the price history. Chart patterns can provide clues regarding how prices might move within the patterns and where they are likely to go after a break-out.